As economic development strategies for developing countries ten year plan unfolds, let’s embark on a journey to explore the very fabric of progress. It’s about more than just numbers; it’s about shaping destinies, fostering hope, and building a future where prosperity isn’t a privilege, but a shared reality. The blueprint for success, while complex, is undeniably within reach. The path ahead is paved with strategic infrastructure investments, unlocking the potential of human capital, and empowering the engines of entrepreneurship.
This comprehensive plan serves as a roadmap, guiding developing nations toward sustainable growth. It navigates the intricacies of attracting investment, embracing technological advancements, and managing resources wisely. We will delve into how effective trade policies, and innovative approaches can catalyze economic transformation, ensuring a future where every nation can flourish and contribute to a more equitable global landscape. This isn’t just a plan; it’s a commitment to building a better world, one strategic initiative at a time.
How can developing nations leverage infrastructure investments to spur long-term economic growth within a decade
Alright, let’s talk about how developing nations can really kickstart their economies through smart infrastructure investments over the next ten years. It’s not just about building things; it’s about building theright* things, the ones that will create a ripple effect of growth, opportunity, and a better future for everyone. We’re aiming for a future where progress isn’t just a buzzword but a lived reality.
Robust Transportation Networks: Facilitating Trade and Connectivity
Think of transportation networks as the veins and arteries of an economy. Without them, goods and people can’t flow, and economic lifeblood stagnates. Improving these networks is absolutely critical.Building and improving transportation networks requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Roads: Paving and maintaining roads is the most basic. Think about the impact of paved roads on farmers getting their goods to market, or tourists being able to easily access destinations. Prioritizing roads that connect rural areas to urban centers is a game-changer.
- Railways: Railways are essential for moving large volumes of goods efficiently and reducing the cost of transportation. Investing in high-speed rail lines can also connect cities and regions, boosting tourism and business travel.
- Ports: Ports are the gateways to global trade. Expanding and modernizing ports to handle larger ships and increased cargo volumes is a necessity for participating in international markets. This includes improving infrastructure such as cargo handling equipment and storage facilities.
The key is to prioritize projects that offer the highest return on investment. This might mean focusing on upgrading existing infrastructure first, rather than starting from scratch. Consider the success story of the Mombasa-Nairobi Standard Gauge Railway in Kenya. This project significantly reduced the cost and time of transporting goods, boosting trade and economic activity in the region. It is important to consider that all of these transportation systems should be integrated to be more efficient.
Energy Infrastructure: Ensuring Stable and Affordable Power Supply
Access to reliable and affordable energy is the lifeblood of any modern economy. Without it, businesses can’t operate, schools can’t function, and people’s lives are drastically limited.Focusing on energy infrastructure involves:
- Power Plants: Investing in power plants, whether they’re fueled by fossil fuels, renewable sources, or a combination, is vital. Consider the energy needs of the population, and ensure the plants are efficient and environmentally sustainable.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower are essential for long-term sustainability. They also offer the advantage of reducing reliance on imported fuels and creating local jobs. Consider the example of Costa Rica, which generates almost all of its electricity from renewable sources.
- Transmission and Distribution Networks: Building and maintaining efficient transmission and distribution networks are just as important as generating power. These networks deliver electricity to homes, businesses, and industrial facilities. This is the infrastructure that needs to be in place for energy access.
It’s important to remember that these investments should be made with an eye toward sustainability. Renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly cost-competitive, and they can play a crucial role in mitigating climate change. A well-planned energy infrastructure plan will create a cleaner, more reliable, and more affordable energy future.
Digital Infrastructure: Promoting Innovation, Education, and Access to Information
Digital infrastructure is the nervous system of the modern economy. It enables communication, education, access to information, and so much more. Without it, developing nations risk being left behind.Key elements of digital infrastructure are:
- Broadband Internet Access: High-speed internet access is essential for businesses, schools, and individuals. Investing in fiber optic cables and other broadband technologies is a priority.
- Mobile Communication Networks: Mobile networks have expanded rapidly in developing countries, and they’re playing an increasingly important role in economic development. Expanding coverage and improving the quality of mobile services is essential.
- Data Centers: As more and more data is generated and consumed, the need for data centers will grow. Investing in data centers can help support local businesses and attract foreign investment.
Think about the impact of mobile money services in countries like Kenya, which have transformed financial inclusion and economic activity. The digital revolution is already underway, and the countries that embrace it will be the ones that thrive.
Successful Infrastructure Projects and Lessons Learned
The key to successful infrastructure projects is careful planning, effective implementation, and a commitment to sustainability. There are several examples of successful infrastructure projects in developing countries, each offering valuable lessons.Here are some lessons to be learned:
- Prioritize projects based on their potential impact on economic growth. This means focusing on projects that will create jobs, boost trade, and improve living standards.
- Involve local communities in the planning and implementation of projects. This can help ensure that projects are tailored to the needs of the community and that they are sustainable in the long term.
- Use public-private partnerships (PPPs) to leverage private sector expertise and financing. PPPs can be a valuable tool for financing infrastructure projects, but it’s important to structure them carefully to ensure that they are fair and transparent.
- Invest in capacity building to ensure that local communities have the skills and knowledge they need to maintain and operate infrastructure projects. This is essential for ensuring that projects are sustainable in the long term.
For example, the construction of the Panama Canal was a monumental feat of engineering that significantly boosted global trade and economic growth in the region. However, the project also faced significant challenges, including cost overruns and environmental concerns. The lessons learned from these projects can be applied to future infrastructure investments, helping to ensure that they are successful and sustainable.
Types of Infrastructure Investments and Their Respective Economic Benefits
Here is a table showcasing types of infrastructure investments and their respective economic benefits:
| Infrastructure Investment | Economic Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Transportation Networks |
|
|
| Energy Infrastructure |
|
|
| Digital Infrastructure |
|
|
What are the most effective strategies for fostering human capital development in developing countries over a ten-year period
Let’s face it, developing countries aren’t just looking for a quick fix; they’re aiming for sustainable prosperity. And the cornerstone of that prosperity? Their people. Investing in human capital isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s the single most impactful thing a nation can do. It’s about cultivating a skilled, healthy, and empowered populace, ready to seize opportunities and drive economic growth.
Over the next decade, a strategic approach to human capital development will be critical.
Investing in Education
Education is the bedrock upon which all other progress is built. A well-educated workforce is more productive, innovative, and adaptable. That’s why it’s vital to focus on education across all levels.Primary education lays the foundation, teaching basic literacy and numeracy skills. Secondary education builds upon this, providing more specialized knowledge and preparing students for higher education or vocational training. Vocational training is particularly important, offering practical skills that directly translate into employment opportunities.The investment in education should include:
- Expanding access: Ensure every child has the opportunity to attend school, regardless of their background or location. This means building schools, training teachers, and providing scholarships and financial aid.
- Improving quality: Focus on improving the quality of education by providing updated curriculum, better teaching materials, and teacher training. This includes incorporating technology and fostering critical thinking skills.
- Aligning with the labor market: Tailor educational programs to the needs of the local economy, ensuring graduates have the skills employers are seeking. This involves partnerships between educational institutions and businesses.
“Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.”
Nelson Mandela
Investing in education is not just about schools and textbooks; it’s about creating a culture of learning and empowering individuals to reach their full potential. Consider the example of South Korea, which, after the Korean War, prioritized education. The result? A highly skilled workforce that fueled rapid economic growth.
Investing in Healthcare
A healthy population is a productive population. Investing in healthcare is essential for economic development, leading to a healthier, more productive, and longer-lived workforce. It also contributes to a better quality of life.Healthcare investments should focus on:
- Improving access to quality healthcare services: This involves building and equipping hospitals and clinics, training healthcare professionals, and ensuring access to essential medicines and treatments, particularly in rural and underserved areas.
- Promoting public health initiatives: Implementing programs to prevent and control diseases, such as vaccination campaigns, sanitation projects, and health education programs.
- Addressing maternal and child health: Focusing on improving maternal and child health outcomes through prenatal care, safe delivery practices, and postnatal care.
The success of a robust healthcare system can be seen in countries like Costa Rica, where a strong public healthcare system has contributed to high life expectancy and a healthy workforce, bolstering economic growth.
Promoting Gender Equality and Empowering Women
Empowering women is not only a matter of social justice; it’s also a smart economic strategy. When women have equal access to education, economic opportunities, and decision-making power, economies thrive.Promoting gender equality and empowering women involves:
- Expanding educational opportunities: Ensuring girls and women have equal access to education at all levels, from primary school to university.
- Promoting economic participation: Creating opportunities for women to participate in the workforce, including access to credit, training, and entrepreneurship programs.
- Addressing gender-based discrimination: Combating gender-based violence and discrimination, and ensuring women’s rights are protected under the law.
Consider Rwanda, which has made significant strides in gender equality in recent years. Women hold a majority of seats in parliament, and the country has implemented policies to promote women’s economic empowerment. This has contributed to significant economic progress.
Examples of Successful Human Capital Development Programs
Several developing countries have demonstrated the positive impact of focused human capital development programs.
- Brazil’s Bolsa Família program: This conditional cash transfer program provides financial assistance to low-income families, provided they meet certain requirements, such as keeping their children in school and attending health check-ups. This has improved education and health outcomes for millions of Brazilians.
- India’s National Rural Health Mission: This program aims to improve healthcare access in rural areas, leading to improved maternal and child health outcomes.
- Bangladesh’s microfinance initiatives: These programs provide small loans to women entrepreneurs, enabling them to start and grow businesses, thereby increasing their economic participation.
Methodologies for Evaluating Program Efficacy
Measuring the impact of human capital development programs is crucial for ensuring they are effective and efficient. Here are three distinct methodologies:
- Impact evaluations: These use rigorous methods, such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or quasi-experimental designs, to assess the causal impact of a program on specific outcomes. For example, an RCT could be used to evaluate the impact of a new education program on student test scores.
- Cost-benefit analysis: This method compares the costs of a program with the benefits it generates, such as increased productivity, improved health outcomes, and reduced poverty.
- Monitoring and evaluation (M&E) systems: These systems track program inputs, outputs, outcomes, and impacts over time, providing valuable data for program improvement and accountability.
These methodologies, when applied diligently, provide the necessary insights to adapt, refine, and ensure the lasting success of human capital development programs.
What role does promoting entrepreneurship and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) play in the economic advancement of developing nations
The engine of any thriving economy, particularly in developing nations, is often the entrepreneurial spirit and the dynamism of small and medium-sized enterprises. SMEs are not just businesses; they are the bedrock upon which sustainable growth is built, providing jobs, fostering innovation, and driving economic diversification. Recognizing and nurturing this sector is paramount for any ten-year economic development strategy.
Creating a Favorable Business Environment
Creating a fertile ground for SMEs means dismantling the barriers that stifle their growth. This requires a concerted effort to streamline processes and eliminate red tape.
- Simplifying Regulations: Overly complex regulations can suffocate nascent businesses. Simplifying business registration, licensing, and permit procedures reduces the time and cost associated with starting and operating a business. Consider the experience of Rwanda, which significantly improved its ease of doing business ranking by simplifying its business registration process, leading to a surge in new SME formations.
- Reducing Bureaucratic Hurdles: Corruption and bureaucratic inefficiencies are significant impediments. Implementing transparent governance practices, reducing the number of steps required to complete a transaction, and embracing digital solutions can significantly reduce the time and cost of doing business. This can include online portals for tax payments, permit applications, and business registration.
- Enforcing the Rule of Law: A strong legal framework that protects property rights, enforces contracts, and provides a fair and impartial judicial system is crucial. This instills confidence in investors and entrepreneurs, encouraging them to invest in their businesses and create jobs.
Providing Access to Finance
The lifeblood of any business is access to capital. SMEs, often lacking the collateral or credit history required by traditional lenders, require alternative financing solutions.
- Microloans: Microloans, small loans typically offered to individuals or small groups, are particularly effective in reaching underserved populations and supporting micro-enterprises. Grameen Bank in Bangladesh is a prime example, providing microloans to millions of people, mostly women, and enabling them to start and grow their businesses.
- Venture Capital: Venture capital firms can provide funding for high-growth potential SMEs, often in innovative sectors. The availability of venture capital can accelerate the growth of promising startups.
- Angel Investors: Angel investors, individuals who invest their own money in startups, can provide both capital and mentorship. They often take a more hands-on approach than venture capitalists, guiding the growth of the businesses they invest in.
Providing Mentorship, Training, and Business Development Services
Beyond finance, SMEs need support in navigating the complexities of the business world. Mentorship, training, and business development services are essential for fostering their success.
- Mentorship Programs: Pairing experienced business professionals with SME owners provides invaluable guidance on business strategy, operations, and financial management.
- Training Programs: Offering training in areas such as financial literacy, marketing, sales, and human resource management equips SME owners with the skills they need to succeed.
- Business Development Services: Providing access to services such as market research, business plan development, and legal advice can help SMEs make informed decisions and navigate challenges.
Successful SME Development Programs and Their Impact
Numerous developing countries have implemented successful SME development programs. These programs demonstrate the significant impact that targeted support can have on economic growth.
- Kenya’s Youth Enterprise Development Fund: This fund provides financial support and business development services to young entrepreneurs, contributing to job creation and economic empowerment.
- India’s Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency (MUDRA) Yojana: This program provides financial support to micro-enterprises, fostering entrepreneurship and contributing to inclusive growth.
- The SME Toolkit from the International Finance Corporation (IFC): This resource provides a wealth of information and tools for SMEs, supporting their growth and development across various sectors.
Model SME Development Program: The “EmpowerUp” InitiativeKey Components:
- Financial Support: Access to microloans (up to $5,000) and seed funding (up to $20,000) for promising startups.
- Mentorship: A network of experienced business professionals providing one-on-one mentoring to SME owners.
- Training: Comprehensive training programs in areas such as financial management, marketing, and digital literacy.
- Business Development Services: Access to market research, business plan development support, and legal advice.
- Incubation Centers: Physical spaces offering shared office facilities, networking opportunities, and access to specialized resources.
Expected Outcomes (within 5 years):
- Creation of 5,000 new SMEs.
- Generation of 20,000 new jobs.
- Increase in SME contribution to GDP by 5%.
- Improvement in the ease of doing business ranking by 10 places.
- Increase in SME export revenue by 15%.
How can developing countries attract and retain foreign direct investment (FDI) to fuel economic growth within a decade

Source: cheggcdn.com
Alright, let’s talk about how developing nations can really amp up their economic game by snagging some serious foreign investment. It’s not just about getting the money; it’s about creating an environment that screams “invest here!” and then making sure those investors stick around for the long haul. It’s a bit like building a solid friendship – you need trust, mutual benefit, and a little bit of sparkle to keep things interesting.
We’re aiming for sustainable growth, folks, not a quick sugar rush.
Establishing a Stable and Predictable Investment Climate
This is the cornerstone, the very foundation upon which you build your FDI empire. Imagine trying to build a skyscraper on quicksand – it’s not going to work. Investors need to feel secure, knowing their investments are safe and that the rules of the game won’t change overnight. A stable climate is non-negotiable.This means having robust legal frameworks, think of it as a solid legal foundation.
It is essential to have laws that are clear, consistent, and fairly enforced. Corruption? We need to stamp that out – it’s a major investor turnoff. And protecting property rights? Absolutely crucial.
Investors need to know their assets are safe from seizure or arbitrary government action. If the government does not respect the law, the investor will not respect the government.
A predictable investment climate breeds confidence, and confidence breeds investment.
In countries like Singapore, a strong legal system, low corruption, and clear property rights have been major drivers of their FDI success. They’ve consistently ranked high in global indices for ease of doing business, making them a magnet for foreign capital.
Offering Tax Incentives and Financial Benefits
Let’s be real, money talks. And sometimes, a little incentive goes a long way in attracting attention. Tax breaks, subsidies, and other financial sweeteners can be powerful tools to lure investors. But, and this is a big but, we need to walk a tightrope here.The key is to balance attractiveness with fairness and transparency. Incentives should be designed to be targeted, temporary, and performance-based.
Avoid blanket benefits that drain the treasury without delivering tangible results. Transparency is crucial; investors need to understand the rules and feel confident that the playing field is level.Consider countries like Ireland, which strategically used tax incentives to attract tech giants. They offered lower corporate tax rates, but the conditions were clear, and the system was relatively easy to navigate.
This approach, while not without controversy, helped transform Ireland into a major tech hub. However, it’s important to learn from the downsides too, such as ensuring that these incentives don’t lead to tax avoidance or create unfair advantages.
Promoting Investment in Specific Sectors
Diversification is the name of the game. Putting all your eggs in one basket is a recipe for disaster. Instead of relying on a single industry, developing nations should strategically target sectors with high growth potential and the ability to create jobs and transfer technology.Manufacturing, technology, and tourism are often prime candidates. Manufacturing can create a base for export-oriented growth.
Technology can drive innovation and productivity gains. Tourism can generate immediate revenue and boost other sectors like hospitality and transportation.
Strategic sector targeting allows countries to tailor their FDI attraction efforts, creating a win-win scenario for both investors and the host nation.
China’s economic transformation is a powerful example. The country’s focus on attracting FDI in manufacturing, particularly in export-oriented industries, has been instrumental in its rapid economic growth. They provided special economic zones with infrastructure and incentives to attract foreign manufacturers.
Let’s dive into the complexities of systems, shall we? The springer advances in intelligent systems and computing rag system offers a fascinating look at cutting-edge research. It’s inspiring to see how innovation can transform our world. Simultaneously, addressing mental health concerns within the publications against us healthcare system mental health is crucial. We must advocate for accessible care, and these publications are a step in the right direction.
Examples of Successful FDI Attraction Strategies
Several developing countries have successfully employed strategies to attract and retain FDI. Here are a few examples:* Vietnam: Vietnam’s consistent economic growth over the past few decades is, in part, due to its strategic FDI attraction policies. They focused on creating a favorable investment climate, offering tax incentives, and investing in infrastructure. The country also prioritized investment in manufacturing, attracting major electronics companies.
This has led to a boom in exports and job creation.* Costa Rica: Costa Rica has successfully leveraged its reputation for environmental sustainability and political stability to attract FDI in the technology and medical device sectors. They have invested heavily in education and training to develop a skilled workforce. They offer attractive tax incentives and a streamlined regulatory process.* Mauritius: Mauritius has transformed itself from a sugar-dependent economy to a diversified one, in large part due to its success in attracting FDI in tourism, financial services, and real estate.
They created a stable political environment, a transparent legal system, and a business-friendly regulatory framework. They have also marketed themselves as a gateway to Africa.
Measuring the Success of FDI Attraction Strategies
Measuring the success of FDI attraction strategies is vital to ensure effectiveness and make necessary adjustments. Here are four key methods:* Increase in FDI Inflows: This is the most straightforward metric. Track the annual amount of FDI entering the country. Analyze trends over time to see if your strategies are working. The higher the amount, the better the strategy.
Job Creation
Assess the number of jobs created directly and indirectly by FDI-funded projects. This is a crucial measure of the economic impact of FDI. Consider the skill level of the jobs created.
Technology Transfer and Innovation
Evaluate the extent to which FDI leads to the transfer of technology, knowledge, and skills. This can be measured through the number of patents filed, research and development expenditures, and the adoption of new technologies by local firms.
Contribution to GDP and Exports
Measure the contribution of FDI to the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and exports. This shows the overall economic impact and the extent to which FDI is driving growth and international trade.
What are the most effective strategies for promoting sustainable economic development in developing countries over a ten-year period: Economic Development Strategies For Developing Countries Ten Year Plan
Okay, so we’ve got a decade to make some serious headway, right? We’re not just aiming for a quick buck; we’re talking about building something that lasts, something that doesn’t wreck the planet in the process. It’s about smart growth – growth that benefits everyone, now and in the future. It’s a challenge, sure, but also a massive opportunity to leapfrog outdated models and build something truly remarkable.
Let’s get into it.
Balancing Economic Growth with Environmental Protection
Look, it’s not either/or. We can’t just bulldoze our way to prosperity. Sustainable resource management and pollution control are absolutely critical. Ignoring the environment is like building a house on quicksand. It’s only a matter of time before everything collapses.Here’s the deal:* Sustainable Resource Management: This means using resources responsibly.
Think about forests, water, and minerals. We need to manage these resources in a way that doesn’t deplete them. For example, sustainable forestry practices, like selective logging and reforestation programs, can help maintain forest cover while providing timber for economic activities. It’s all about long-term planning.
Pollution Control
We need to keep our air and water clean. That means investing in wastewater treatment plants, enforcing emission standards for factories, and promoting cleaner technologies. Consider the case of Curitiba, Brazil, a city renowned for its innovative urban planning, including an integrated public transportation system and extensive green spaces. This has significantly reduced air pollution and improved the quality of life for its residents.
“Environmental protection isn’t just about being ‘green’; it’s about ensuring economic viability.”
Circular Economy Principles
Moving away from a “take-make-dispose” model to a circular economy, where resources are reused and recycled, is crucial. This reduces waste, conserves resources, and creates new economic opportunities.
Promoting Green Technologies and Renewable Energy
Embracing green tech and renewable energy is not just a feel-good measure; it’s a smart economic move. It’s about reducing our carbon footprint, creating jobs, and becoming more energy independent. It’s about the future.Here’s the breakdown:* Investing in Solar, Wind, and Hydropower: These are proven technologies that are becoming increasingly affordable. Governments can incentivize these investments through subsidies, tax breaks, and feed-in tariffs.
For example, Costa Rica generates nearly all of its electricity from renewable sources, demonstrating the feasibility of transitioning to a green energy system.
Promoting Energy Efficiency
This means making buildings, industries, and transportation more energy-efficient. Simple things like improving building insulation, using LED lighting, and promoting public transportation can make a huge difference.
Developing Green Tech Industries
Supporting the growth of industries that develop and manufacture green technologies can create new jobs and export opportunities. Think of the potential for manufacturing solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicle components.
Investing in Climate Change Adaptation and Resilience Measures
Climate change is happening, and we need to be prepared. This means investing in measures that help us adapt to the impacts of climate change and build resilience.Here’s how we can do it:* Drought-Resistant Agriculture: Developing and promoting drought-resistant crops and improving irrigation techniques are essential for food security. This is particularly important in regions prone to droughts.
Disaster Preparedness
Investing in early warning systems, building infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events, and training communities on how to respond to disasters can save lives and reduce economic losses. The Netherlands, with its advanced flood defense systems and comprehensive disaster management plans, is a prime example of how to build resilience against climate-related threats.
Coastal Protection
Protecting coastal communities from rising sea levels and storm surges is critical. This can involve building seawalls, restoring mangrove forests, and implementing land-use planning regulations.
Examples of Successful Sustainable Development Initiatives and Their Impact
Let’s look at some real-world examples of how developing countries are making sustainable development a reality. These initiatives show that it’s possible to achieve economic growth while protecting the environment.* Bhutan: This small Himalayan kingdom is carbon-negative, meaning it absorbs more carbon dioxide than it emits. This is due to its commitment to preserving its forests and generating hydropower.
The impact? A clean environment, a thriving tourism sector, and a high quality of life.
Rwanda
Rwanda has implemented a comprehensive green growth strategy, focusing on renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and environmental conservation. The result is impressive economic growth, improved environmental conditions, and a reputation as a leader in sustainable development.
Vietnam
Vietnam’s investment in renewable energy, particularly solar power, has not only reduced its carbon emissions but also created thousands of jobs and attracted significant foreign investment.Here’s a table summarizing specific sustainable development initiatives and their benefits:
| Initiative | Description | Expected Environmental Benefits | Expected Economic Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Power Plant Development | Construction and operation of utility-scale solar power plants. | Reduced greenhouse gas emissions, decreased air pollution, conservation of fossil fuels. | Creation of construction and operation jobs, reduced energy costs, increased energy independence. |
| Sustainable Forestry Programs | Implementing selective logging, reforestation, and forest management practices. | Preservation of biodiversity, carbon sequestration, reduced soil erosion. | Sustainable timber production, eco-tourism opportunities, improved water quality. |
| Waste Recycling and Management Systems | Establishing recycling facilities, composting programs, and waste reduction initiatives. | Reduced landfill waste, decreased pollution, conservation of resources. | Creation of recycling jobs, sale of recycled materials, reduced waste disposal costs. |
| Drought-Resistant Agriculture | Promoting the use of drought-resistant crops, improved irrigation techniques, and water conservation methods. | Increased food security, reduced water usage, soil conservation. | Higher crop yields, reduced crop failure, increased farmer incomes. |
How can developing countries effectively manage and utilize natural resources to support economic growth and development within a ten-year plan

Source: slideteam.net
Alright, let’s talk about something super important: how developing nations can actuallywin* with their natural resources. It’s not just about digging stuff up and selling it; it’s about playing the long game, building a strong economy, and ensuring a better future for everyone. This is about turning what’s in the ground into prosperity, but doing it the right way. We’re talking smart, sustainable, and equitable resource management.
Implementing Responsible Resource Extraction Practices
This is the bedrock. Without it, you’re building on sand. Responsible extraction means doing things in a way that minimizes damage to the environment and protects the people who do the work. It’s not just about ticking boxes; it’s about a fundamental shift in mindset.Here’s what that looks like in practice:* Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs): Before a project even starts, thoroughly assess the potential environmental consequences.
This isn’t just a formality; it’s a critical tool for informed decision-making. It’s about understanding the risks and planning for mitigation from the get-go. Imagine the potential impact on water resources, air quality, and biodiversity. EIAs help identify and address these concerns proactively.* Rehabilitation and Restoration: When extraction ends, the land needs to be put back, as close as possible, to its original state.
This involves reforestation, soil remediation, and habitat restoration. Think about the long-term benefits: preventing erosion, protecting water sources, and creating opportunities for ecotourism.* Fair Labor Standards: Workers in the natural resource sector deserve fair wages, safe working conditions, and the right to organize. This isn’t just about ethics; it’s about creating a skilled and motivated workforce. Consider the positive impact on local communities when jobs are secure, and workers are treated with respect.* Community Engagement: Before, during, and after extraction, involve local communities in the decision-making process.
This means consulting with them, addressing their concerns, and ensuring they benefit from the resources being extracted. It’s about building trust and fostering a sense of shared ownership. Think about how this can lead to reduced conflict and increased social cohesion.* Waste Management: Proper handling and disposal of waste products is essential. This includes reducing waste generation, recycling, and safely disposing of any remaining waste.
This is not just about avoiding environmental damage; it’s about protecting public health.
Investing in Value-Added Processing of Natural Resources
Raw materials are like unfinished products. They’re valuable, but they’remuch* more valuable when you add value to them. This means transforming raw materials into finished or semi-finished products, like manufacturing or refining.Think of it this way: selling unprocessed minerals is like selling raw ingredients. You’re missing out on the profits from baking the cake.* Manufacturing: Developing manufacturing capabilities allows countries to process raw materials into products for domestic consumption and export.
This can include things like building factories to produce steel from iron ore, or aluminum from bauxite.* Refining: Refining processes can transform raw materials into higher-value products. For example, crude oil can be refined into gasoline, diesel, and other fuels.* Training and Skills Development: Investing in education and training programs is crucial. This ensures the workforce has the skills needed to operate and maintain the value-added processing facilities.
It is about equipping people with the expertise to take on new opportunities.* Infrastructure Development: Building roads, ports, and energy infrastructure is essential to support value-added processing. Without this, you can’t get the raw materials in or the finished products out efficiently.* Technology Transfer: Partnering with international companies or institutions to transfer technology and expertise can help developing countries accelerate their value-added processing capabilities.
Establishing Transparent Governance Structures and Combating Corruption
This is the key to unlocking the full potential of natural resources. Without transparency and accountability, the benefits of resource wealth can be siphoned off, leaving the country and its people worse off.Here’s why it’s so critical:* Transparency: Open and accessible information about contracts, payments, and revenues helps prevent corruption and ensures that resource wealth benefits the entire population.
For instance, imagine a public online database that displays all government contracts related to natural resource extraction. This would empower citizens and civil society organizations to monitor deals and hold government accountable.* Accountability: Clear rules and regulations, along with independent oversight bodies, are essential to ensure that resource revenues are managed responsibly. Consider the creation of an independent revenue oversight board with the authority to audit and review all payments related to natural resources.
Thinking long-term is key. That’s why the 10-year socio-economic development strategy regulatory reform demands our attention. It’s a blueprint for growth, and it’s imperative we understand its implications. Consider the impact on businesses, such as the advance auto parts computer system benchmark , and how technology shapes efficiency. Finally, let’s look at how Singapore has successfully built its economy with the singapore economic development strategy playbook , showing us the potential for strategic planning.
This board would report its findings to the public and hold those who misuse funds accountable.* Combating Corruption: Corruption undermines good governance and diverts resources away from development. Anti-corruption measures, such as strong legal frameworks and independent anti-corruption agencies, are crucial. Imagine a government agency dedicated to investigating and prosecuting corruption in the natural resource sector.
This agency would be equipped with the resources and authority to pursue cases of bribery, fraud, and embezzlement.* Public Participation: Engaging citizens and civil society organizations in the decision-making process helps ensure that resource management policies reflect the needs and priorities of the people.
Consider holding public forums and consultations to discuss proposed mining projects, giving citizens the opportunity to voice their concerns and influence decisions.
* International Cooperation: Working with international organizations and other countries can help strengthen governance structures and combat corruption.
For example, participating in initiatives like the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI) can help countries improve their transparency and accountability in the natural resource sector.
Examples of Successful Natural Resource Management Strategies in Developing Countries and Their Impact
Let’s look at a few examples of how this can work in the real world.* Botswana and Diamonds: Botswana has used its diamond wealth to invest in education, healthcare, and infrastructure, leading to significant economic growth and a high standard of living. The key was transparent governance, a focus on long-term development, and wise investment of resource revenues. Botswana’s success is a powerful example of how natural resources can be a blessing, not a curse.* Norway and Oil: While not a developing country, Norway’s model of managing its oil wealth provides valuable lessons.
They established a sovereign wealth fund to save and invest oil revenues for future generations. This has helped stabilize the economy and provide a safety net. The lesson? Planning for the future and avoiding short-term gains is crucial.* Chile and Copper: Chile has used its copper resources to diversify its economy and invest in human capital. By focusing on education and innovation, they’ve created a more resilient economy that’s less reliant on a single commodity.
Chile’s experience highlights the importance of looking beyond the immediate benefits of resource extraction.* Ghana and Cocoa: While not strictly natural resources, Ghana’s success in promoting its cocoa industry is worth mentioning. By investing in fair trade practices, promoting sustainable farming, and supporting local farmers, Ghana has been able to increase its cocoa revenues and improve the livelihoods of its farmers.
This shows the value of empowering local communities and supporting sustainable practices.These examples highlight that successful natural resource management isn’t just about the resources themselves; it’s about the policies, the governance, and the vision for the future.
Five Essential Components of a Robust Natural Resource Management Framework
Here’s a quick checklist for building a solid foundation:* Strong Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Clear laws and regulations that govern resource extraction, environmental protection, and community rights. This creates a level playing field and prevents corruption.
Transparent Governance
Open and accountable institutions, including independent oversight bodies and mechanisms for public participation. This builds trust and ensures that resource revenues are used for the benefit of all.
Sustainable Extraction Practices
Implementing environmentally sound extraction methods, minimizing environmental damage, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of resources. This protects the environment and the communities that depend on it.
Value-Added Processing
Investing in infrastructure, technology, and skills development to process raw materials into higher-value products. This creates jobs, boosts economic growth, and increases export revenues.
Community Engagement and Benefit-Sharing
Involving local communities in the decision-making process and ensuring they benefit from resource extraction through jobs, infrastructure development, and revenue sharing. This fosters social cohesion and ensures that resource wealth is distributed equitably.
What are the key considerations for implementing effective trade policies to promote economic growth in developing countries over a ten-year period
Source: isu.pub
Alright, let’s talk trade! It’s the lifeblood of global economic growth, especially for developing nations. Getting trade policies right isn’t just about signing a few deals; it’s about building a whole ecosystem that supports sustainable growth and resilience. Over the next decade, smart trade strategies can unlock incredible opportunities, but it requires careful planning and execution.
Diversifying Exports and Reducing Reliance on Primary Commodities, Economic development strategies for developing countries ten year plan
The path to economic resilience begins with a diverse export basket. Relying solely on a few primary commodities is a recipe for vulnerability. When commodity prices fluctuate – and they always do – your entire economy can be thrown off balance. Think of it like putting all your eggs in one basket, and that basket has a hole!To break free, countries need to actively promote the diversification of their exports.
This means investing in industries beyond raw materials. Supporting manufacturing, services, and value-added processing is crucial. It also means encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship, which can lead to the creation of new, high-value exports. For instance, consider Côte d’Ivoire, which, despite being a major cocoa producer, has been working to increase the export of processed cocoa products, adding value and creating more stable revenue streams.
This is not just about selling more products; it’s about building a more stable and prosperous future.
Negotiating Favorable Trade Agreements
Market access is king. Without it, even the most competitive products can’t reach global consumers. That’s where smart trade agreements come in. Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and regional trade pacts open doors to new markets, reduce tariffs, and create opportunities for businesses to grow.However, it’s not just about signing agreements; it’s about negotiating favorable terms. This requires skilled negotiators who understand the nuances of international trade and are prepared to advocate for their country’s interests.
They must be ready to push for provisions that support domestic industries, protect intellectual property, and promote fair labor standards. Consider the example of Vietnam, which has successfully leveraged its participation in the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) to boost its exports and attract foreign investment. This agreement provides preferential access to several key markets and has been a significant driver of Vietnam’s economic growth.
Investing in Trade Facilitation Measures
Even the best trade agreements are useless if it’s difficult and expensive to move goods across borders. That’s where trade facilitation comes in. Streamlining customs procedures, improving logistics infrastructure, and reducing red tape are essential to reduce trade costs and boost efficiency.This includes investing in modern ports, efficient transportation networks, and digital platforms that simplify trade processes. It also means adopting international best practices, such as the World Trade Organization’s Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA), which provides a framework for streamlining customs procedures.
For example, Rwanda has significantly improved its trading environment by implementing single-window systems for customs clearance and investing in road infrastructure, leading to reduced transit times and lower trade costs.
Examples of Successful Trade Policies in Developing Countries and Their Impact
Many developing countries have successfully used trade policies to fuel economic growth.* South Korea: In the 1960s and 1970s, South Korea focused on export-led growth, investing heavily in manufacturing and targeting key export markets. This strategy, coupled with strategic trade agreements, transformed the country into a global economic powerhouse.* Singapore: Singapore’s open trade policies and investments in trade facilitation have made it a global trading hub.
Its strategic location, efficient port, and business-friendly environment have attracted significant foreign investment and fueled economic growth.* Mauritius: Mauritius has leveraged its participation in various trade agreements, including the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) and the COMESA Free Trade Area, to diversify its economy and boost its exports.These examples show that strategic trade policies can have a profound impact on economic development.
They highlight the importance of diversification, favorable trade agreements, and investments in trade facilitation.
Three Critical Steps in Negotiating a Beneficial Trade Agreement
Negotiating a successful trade agreement is a complex process, but these three steps are essential:* Conduct Thorough Research and Analysis: Before entering negotiations, conduct detailed research on the potential benefits and risks of the agreement. This includes assessing the impact on different sectors of the economy, identifying key negotiating priorities, and understanding the negotiating positions of other parties.* Build a Strong Negotiating Team: Assemble a skilled negotiating team with expertise in trade law, economics, and international relations.
The team should be able to advocate for the country’s interests effectively and navigate the complexities of trade negotiations.* Prioritize National Interests and Flexibility: Define clear negotiating objectives and prioritize the country’s national interests. However, be prepared to show flexibility and make compromises to reach a mutually beneficial agreement. The ability to adapt to changing circumstances is crucial for success.
How can developing nations leverage technology and innovation to drive economic transformation within a ten-year timeframe
Let’s be honest, the future is digital, and for developing nations, embracing technology and innovation isn’t just an option – it’s a necessity for leaping forward. Within a decade, the smart play isn’t to catch up; it’s to redefine the game. We’re talking about a complete economic overhaul, powered by the very tools that are shaping the world. It’s about crafting a future where progress isn’t just possible, it’s inevitable.
Investing in Research and Development
Funding research and development is the cornerstone of technological advancement. It’s the lifeblood that feeds innovation, allowing nations to cultivate homegrown solutions and compete on a global stage. Think of it as planting the seeds of future prosperity.Investing wisely means:
- Funding Universities and Research Institutions: Universities and research institutions become hubs of innovation. They attract top talent, fostering collaboration and pushing the boundaries of knowledge. Think of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the United States. MIT is a prime example of how consistent investment in research and development, especially in fields like engineering and computer science, has led to groundbreaking innovations and economic growth.
They attract top talent and foster collaboration.
- Supporting Private Sector Innovation: Encouraging private sector participation through tax incentives, grants, and public-private partnerships can create a dynamic environment for entrepreneurs and businesses. This creates a vibrant ecosystem where ideas flourish and commercialization thrives. Consider South Korea’s approach to supporting its technology giants like Samsung and LG. The government provided early support and incentives, which helped these companies become global leaders in electronics and technology.
Promoting Digital Literacy and Technology Training
A skilled workforce is the engine that drives technological transformation. It’s about equipping people with the knowledge and skills to navigate and thrive in the digital age.This involves:
- Enhancing Workforce Capabilities: Implementing comprehensive digital literacy programs that cover basic computer skills, coding, data analysis, and digital marketing.
- Providing Access to Technology Training Programs: Offering vocational training, online courses, and apprenticeships to equip individuals with the skills needed for emerging technologies. This ensures the workforce is prepared for the jobs of tomorrow. Consider the example of Rwanda, which has made significant strides in promoting digital literacy through its “Connect Rwanda” initiative, providing internet access and digital skills training to its citizens.
Creating a Supportive Ecosystem for Startups and Technology Entrepreneurs
Cultivating a vibrant startup ecosystem is about creating an environment where innovation can flourish. It’s about providing the resources and support that startups need to grow and succeed.Key elements include:
- Access to Funding: Establishing venture capital funds, angel investor networks, and crowdfunding platforms to provide startups with the financial resources they need.
- Mentorship and Incubation Programs: Offering mentorship from experienced entrepreneurs, access to co-working spaces, and incubation programs to help startups refine their business models and strategies. Think of the success of Silicon Valley in the United States. The concentration of venture capital, mentorship, and networking opportunities has been a critical factor in its success.
Examples of Successful Technology and Innovation Initiatives
Real-world examples demonstrate the transformative power of technology and innovation in developing nations.
- M-Pesa in Kenya: M-Pesa, a mobile money transfer service, revolutionized financial inclusion in Kenya. It enabled millions of unbanked people to access financial services, boosting economic activity and reducing poverty.
- E-commerce Platforms in Nigeria: The growth of e-commerce platforms like Jumia and Konga has facilitated trade and entrepreneurship in Nigeria. These platforms have created new opportunities for businesses and consumers.
- India’s Digital Public Infrastructure: India’s investment in digital public infrastructure, including the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and the Aadhaar biometric identification system, has significantly improved financial inclusion, streamlined government services, and fostered innovation in various sectors.
Technology-Driven Economic Transformation Program: “Digital Leap” Key Elements:
- National Digital Infrastructure: Investing in high-speed internet access, cloud computing infrastructure, and data centers across the country.
- Digital Skills Development: Implementing comprehensive digital literacy programs for all citizens, with a focus on coding, data science, and digital marketing. Offering vocational training and online courses to enhance workforce capabilities.
- Startup Ecosystem Support: Establishing venture capital funds, angel investor networks, and incubation programs to support technology startups. Providing mentorship and access to co-working spaces.
- E-Governance and Digital Services: Developing online platforms for government services, including tax payments, business registration, and healthcare access.
- Industry-Specific Innovation Hubs: Creating specialized innovation hubs for key sectors like agriculture, healthcare, and manufacturing, fostering collaboration between researchers, entrepreneurs, and industry experts.
Expected Outcomes:
- Increased GDP growth and job creation, particularly in the technology and digital sectors.
- Improved access to essential services, such as healthcare, education, and financial services.
- Enhanced competitiveness in the global economy, attracting foreign investment and promoting exports.
- Increased financial inclusion, empowering individuals and small businesses.
- A more skilled and adaptable workforce, ready for the challenges of the future.
Final Conclusion
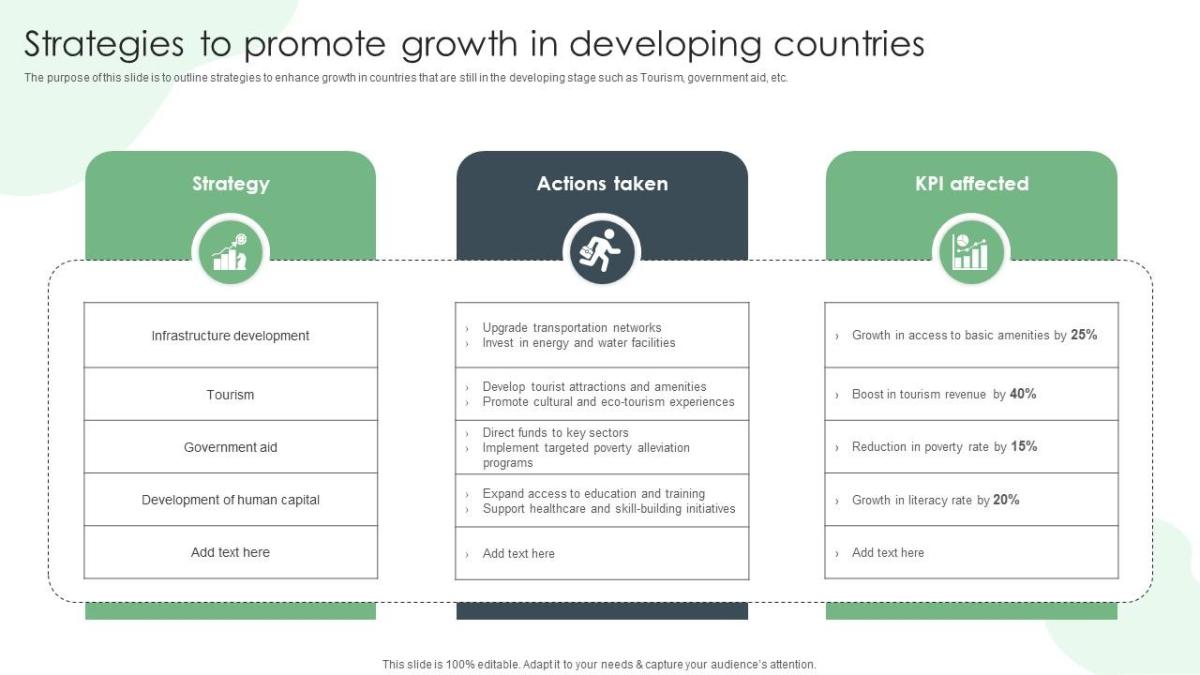
Source: slideteam.net
In wrapping up our exploration of economic development strategies for developing countries ten year plan, it’s clear that the journey towards prosperity is a multifaceted endeavor. The plan we’ve Artikeld, from infrastructure to trade, is more than just a set of policies; it’s a call to action, a testament to the power of collaboration, and a promise of a brighter tomorrow.
Embrace the possibilities, seize the opportunities, and let us together build a future where every nation can thrive, where every citizen can dream, and where the promise of a better world becomes a tangible reality. The future is within our grasp; let’s build it together, with determination, wisdom, and an unwavering belief in the power of progress.