Economic growth strategies for developing countries trends 2025 – it’s not just about numbers; it’s about people, potential, and the promise of a better tomorrow. Imagine a world where innovation thrives, opportunities abound, and the dreams of millions take flight. We’re diving into the heart of what it takes to build vibrant, sustainable economies. The journey to 2025 is a thrilling one, full of challenges and triumphs, and together, we’ll uncover the keys to unlocking unprecedented progress.
This isn’t just a theoretical exercise; it’s a call to action. We’ll explore the critical role of smart governmental policies, from crafting the right fiscal and monetary frameworks to fostering a favorable trade environment. We will see how developing nations can leap forward by harnessing the power of technology, from digital infrastructure to the development of a skilled workforce, and witness the potential for innovation to transform sectors like agriculture, healthcare, and finance.
Moreover, we’ll delve into innovative financing models, like public-private partnerships and the strategic use of foreign direct investment, while navigating the complexities of global value chains and regional integration. And most importantly, we’ll examine how to ensure that growth is inclusive, that it reaches every corner of society, and that poverty is dramatically reduced, paving the way for a future where everyone has the chance to thrive.
What are the pivotal governmental policies required to foster sustainable economic expansion in emerging economies by 2025?

Source: sustainalytics.com
Alright, let’s get down to brass tacks. Developing countries, the engines of tomorrow, need a well-oiled machine to truly take off. That means smart governmental policies, not just a wish and a prayer. We’re talking about a strategic roadmap, a game plan that balances growth with stability, opportunity with responsibility. It’s about creating an environment where businesses can flourish, people can thrive, and the future is something to look forward to.
Essential Fiscal Policies for Long-Term Growth
Fiscal policy is the backbone, the financial compass guiding the ship. It’s about making sure the money flows where it needs to go to create lasting prosperity. This involves careful consideration of taxation, government spending, and debt management.To begin with, a progressive tax system is essential. This ensures that those who can afford to contribute more, do. It funds vital public services, from education and healthcare to infrastructure projects.
Think of it as investing in the future, building the foundation for a more equitable and prosperous society.Government spending, on the other hand, should be targeted. Infrastructure development, such as building roads, bridges, and power grids, creates jobs and unlocks economic potential. Investing in education and skills training equips the workforce with the tools they need to compete in the global marketplace.Debt management is equally crucial.
Overspending and unsustainable debt levels can cripple an economy, leading to financial instability and hindering growth. Prudent borrowing, coupled with responsible fiscal management, ensures that debt remains manageable and doesn’t become a burden on future generations. Consider the example of South Korea in the decades following the Korean War. They focused on strategic investments in education and infrastructure, coupled with responsible debt management, which propelled their economic growth.
They built a strong economy.Furthermore, fiscal policy should be counter-cyclical, meaning it should act as a stabilizer during economic downturns. During recessions, governments can increase spending or cut taxes to stimulate demand and prevent a deeper crisis. During periods of rapid growth, they can implement fiscal restraint to avoid overheating the economy and control inflation.
For example, in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, many developing nations implemented fiscal stimulus packages to mitigate the impact of the global recession.
This included infrastructure projects, tax cuts, and social safety nets, which helped to cushion the blow and support economic recovery.
Remember, the goal is not just to achieve short-term gains but to lay the groundwork for sustainable, long-term growth.
Monetary Policies and Economic Trajectories
Monetary policy, the central bank’s playbook, is about controlling the money supply and credit conditions to influence inflation and economic activity. Interest rate adjustments and currency interventions are the key instruments in this game.Interest rate adjustments are the primary tool. Lowering interest rates encourages borrowing and investment, stimulating economic activity. Conversely, raising interest rates can curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive.
Currency interventions, on the other hand, involve the central bank buying or selling its own currency in the foreign exchange market to influence its value. A weaker currency can boost exports by making them cheaper for foreign buyers, while a stronger currency can help control inflation by making imports cheaper.
The impact of these policies on developing nations’ economic trajectories can be significant.
A well-managed monetary policy can help to stabilize the economy, control inflation, and promote sustainable growth. However, poorly managed policies can lead to financial instability, currency crises, and economic downturns.
For example, the Asian Financial Crisis of 1997-98 highlighted the vulnerability of some developing nations to currency speculation and financial contagion. Countries with weak monetary policies and unsustainable exchange rate regimes were particularly hard hit.
Therefore, it is crucial for central banks in developing nations to adopt credible and transparent monetary policies, with a focus on maintaining price stability and fostering a stable financial environment. This requires a combination of sound policy frameworks, effective communication, and a commitment to independence from political influence.
Trade Policies and the Economic Landscape
Trade policies shape a nation’s place in the global economy, influencing everything from exports to foreign investment. The key tools here are tariffs, trade agreements, and export promotion strategies.Tariffs, taxes on imported goods, can protect domestic industries from foreign competition. However, they can also raise prices for consumers and reduce the competitiveness of domestic exporters.Trade agreements, on the other hand, are pacts between countries to reduce or eliminate trade barriers, such as tariffs and quotas.
They can boost trade, investment, and economic growth by creating larger markets and reducing trade costs.Export promotion strategies involve government programs designed to encourage domestic businesses to sell their goods and services in foreign markets. This can include providing financial assistance, trade missions, and market information.Here’s a comparison of different policy approaches:
| Policy Approach | Description | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Tariffs | Imposing significant taxes on imported goods. | Protection of domestic industries, increased government revenue. | Higher prices for consumers, reduced competitiveness of domestic exporters, potential for trade wars. |
| Free Trade Agreements | Reducing or eliminating trade barriers between countries. | Increased trade and investment, lower prices for consumers, greater access to foreign markets. | Increased competition for domestic industries, potential job losses in some sectors. |
| Export Promotion Strategies | Government programs to encourage exports. | Increased exports, economic growth, job creation, improved balance of payments. | Requires government resources, potential for market distortions, risk of retaliation from trading partners. |
| Import Substitution | Policies aimed at replacing imports with domestically produced goods. | Development of domestic industries, reduced reliance on foreign suppliers. | Higher prices for consumers, reduced competitiveness, potential for inefficiency and rent-seeking. |
The most successful developing economies have adopted a balanced approach to trade policy, combining elements of protectionism with openness to trade and investment. They’ve used tariffs strategically to protect infant industries while also pursuing trade agreements to expand market access. They’ve invested in export promotion strategies to help domestic businesses compete in the global marketplace. Consider the case of Vietnam, which implemented a series of economic reforms, including trade liberalization, to foster export-led growth.
This strategic approach helped them become a major exporter of goods, particularly in the manufacturing sector.
It’s all about finding the right mix, the sweet spot that allows a nation to harness the benefits of globalization while protecting its domestic industries and promoting sustainable economic growth.
How can developing nations effectively leverage technological advancements to accelerate their economic development plans?

Source: slideteam.net
Now, let’s talk about something that hits close to home: healthcare. Understanding us healthcare spending public vs private reform ideas Unveiling the Path to a Healthier Future is crucial. We need to embrace innovative solutions and make healthcare accessible to everyone.
The future of developing nations is inextricably linked to their ability to embrace and harness the power of technology. It’s not just about adopting gadgets; it’s about fundamentally transforming economies, empowering citizens, and building a more prosperous future. The path to sustained economic growth in these countries now hinges on strategically integrating technological advancements into every facet of their development plans.
This is not merely an option, but a necessity.
Digital Infrastructure as a Driver of Economic Progress
A robust digital infrastructure is the bedrock upon which developing nations can build their technological future. It’s the essential foundation for economic expansion in the 21st century. This infrastructure goes beyond just having internet access; it encompasses a holistic ecosystem that supports digital inclusion and economic activity.
- Internet Access: Expanding affordable and reliable internet access is paramount. This involves investing in broadband infrastructure, satellite technologies, and initiatives that reduce the cost of internet services. Consider the impact in Rwanda, where investments in 4G networks significantly boosted mobile internet penetration, enabling access to information, education, and financial services for a broader population.
- Mobile Technology: The ubiquity of mobile phones offers a unique opportunity for developing nations to leapfrog traditional infrastructure barriers. Mobile technology provides access to a variety of services, including mobile banking, agricultural information, and telemedicine. In Kenya, M-Pesa revolutionized mobile money transfer, demonstrating how mobile technology can facilitate financial inclusion and empower individuals.
- E-commerce Platforms: E-commerce platforms create new avenues for businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), to reach wider markets and participate in the global economy. These platforms provide access to customers and supply chains, facilitating trade and economic growth. The growth of e-commerce in countries like Nigeria, driven by platforms such as Jumia, showcases how these platforms can fuel economic diversification and create jobs.
Investing in Human Capital for Technological Proficiency
Technology is only as effective as the people who use it. Therefore, investing in human capital through education and training programs is crucial to ensure a skilled workforce capable of utilizing and adapting to new technologies. This requires a multi-pronged approach.
- Education Reform: Educational systems must be updated to incorporate digital literacy, coding skills, and technology-related subjects. This will prepare the next generation for the demands of a technology-driven economy.
- Vocational Training: Targeted vocational training programs are needed to equip individuals with the specific skills required by various sectors, such as IT support, software development, and digital marketing.
- Lifelong Learning: Continuous learning and upskilling initiatives are essential to ensure that the workforce remains relevant and adaptable as technology evolves. This includes online courses, workshops, and mentorship programs.
Technological Applications Across Sectors
Technology is already transforming various sectors in developing countries, driving efficiency, innovation, and economic growth. Here are some specific examples:
- Agriculture:
- Precision Farming: Drones and sensors are used to monitor crops, optimize irrigation, and apply fertilizers more efficiently, increasing yields and reducing costs. For example, in Ghana, precision farming techniques are helping cocoa farmers improve their harvests and livelihoods.
- Mobile Apps for Farmers: Mobile applications provide farmers with access to real-time market prices, weather forecasts, and agricultural advice, empowering them to make informed decisions. In India, apps like IFFCO Kisan provide crucial information to farmers.
- Healthcare:
- Telemedicine: Telemedicine platforms connect patients in remote areas with doctors and specialists, improving access to healthcare services. In Bangladesh, telemedicine is providing essential medical care to underserved populations.
- Mobile Health (mHealth): Mobile apps and devices are used to monitor patient health, provide health education, and manage chronic diseases. The use of mHealth in Rwanda to track maternal health is a powerful example.
- Finance:
- Mobile Banking and Fintech: Mobile banking and fintech platforms are expanding access to financial services, particularly for the unbanked population. M-Pesa in Kenya serves as a prime example.
- Digital Payments: Digital payment systems reduce transaction costs, increase efficiency, and promote financial inclusion. The rapid adoption of digital payments in countries like India is a testament to their impact.
What innovative financing mechanisms can be implemented to support infrastructure development and attract foreign investment in developing countries by the year 2025?

Source: brookings.edu
It’s time to talk about the lifeblood of progress: financing. Infrastructure is the backbone of any thriving economy, and by 2025, developing nations need creative, forward-thinking ways to fund their growth. This isn’t just about building roads; it’s about building futures. Let’s dive into the most promising avenues for attracting the investment needed to make that happen.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) in Infrastructure
Public-Private Partnerships, or PPPs, have emerged as a crucial model for infrastructure development. They offer a way for governments to leverage private sector expertise and capital. However, like any powerful tool, PPPs come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages.PPP’s offer governments a way to access private capital and expertise, leading to more efficient project delivery and better quality infrastructure.
This often results in projects being completed faster and within budget, thanks to the private sector’s focus on profitability and efficiency. The transfer of risk from the government to the private sector is also a significant advantage, reducing the financial burden on taxpayers if the project faces challenges. For example, in India, the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation utilized a PPP model to rapidly expand its metro system, significantly improving public transportation and reducing traffic congestion.However, PPPs aren’t a magic bullet.
They can be complex to structure, requiring extensive legal and regulatory frameworks. The selection process for private partners needs to be transparent and free from corruption, or the entire project can be compromised. There’s also the risk of higher costs for users due to the need for the private sector to recoup its investment. Furthermore, disputes between the public and private partners can delay or even derail projects.
Let’s be honest, the journey toward prosperity, as detailed in the Economic Development and Poverty Reduction Strategy Rwanda Definition A Journey to Prosperity , is never easy. But, the determination of Rwanda offers a powerful lesson: with the right strategies, we can build a better future.
In many African countries, poorly structured PPPs have led to financial losses and stalled infrastructure projects due to lack of proper risk assessment and oversight.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Economic Growth
Foreign Direct Investment is a key ingredient in the economic recipe for developing nations. But not all FDI is created equal. The type of investment makes a world of difference in terms of its impact on growth.The difference lies in how FDI enters the market. Greenfield investments, where a company establishes a new operation in a foreign country, often create more jobs, transfer technology, and boost overall productivity.
Finally, let’s look at the players in the healthcare market. Navigating the complexities of the sector, as shown by Publicly Traded Healthcare Companies in the US Navigating Reforms Waves , requires a proactive approach. Adapting to changes is key to success in the long run. It’s a chance to improve the entire industry.
This type of investment brings fresh capital and expertise, which can significantly improve the local workforce’s skills and knowledge base. Consider the example of the automotive industry in Vietnam, where significant greenfield investments by global manufacturers have created thousands of jobs and boosted the country’s manufacturing capacity.Mergers and acquisitions (M&A), where a foreign company acquires an existing local business, can also bring benefits, such as access to new markets and technologies.
However, the impact of M&A on job creation and technology transfer can be less pronounced. Sometimes, M&A can even lead to job losses or the closure of local businesses. For example, in the Philippines, some M&A deals in the telecommunications sector have resulted in consolidation, potentially reducing competition and innovation.
Speaking of important comparisons, the data in Public Healthcare GDP US vs. OECD Explained – A Comparative Analysis paints a clear picture. We must analyze what works elsewhere and strive for more efficient and equitable systems. It’s a challenge, but a necessary one.
Accessing International Financial Institutions (IFIs)
International Financial Institutions (IFIs) like the World Bank and the IMF are critical sources of funding for developing countries. Securing funding requires a clear understanding of the procedures and requirements.
- Identify Funding Needs: The first step is a thorough assessment of your country’s infrastructure needs and development priorities. This should include detailed project proposals, feasibility studies, and environmental impact assessments.
- Develop a Strong Project Proposal: A well-prepared proposal is the cornerstone of any successful funding application. It should clearly Artikel the project’s objectives, expected outcomes, financial projections, and implementation plan.
- Meet Eligibility Criteria: Each IFI has its own set of eligibility criteria, including factors like the country’s economic performance, governance, and commitment to reform. Meeting these criteria is essential.
- Prepare the Necessary Documentation: This includes financial statements, legal documents, and environmental and social impact assessments.
- Engage in Negotiations: Once the application is submitted, you’ll need to negotiate the terms of the loan or grant with the IFI. This often involves agreeing to specific policy reforms or conditions.
- Implement and Monitor the Project: After the funding is approved, the project must be implemented according to the agreed-upon plan. Regular monitoring and reporting are crucial to ensure that the project stays on track and achieves its objectives.
- Adhere to Reporting Requirements: IFIs require regular reports on project progress, financial performance, and compliance with environmental and social safeguards.
IFIs often offer technical assistance to help developing countries navigate the funding process. By understanding the procedures and meeting the requirements, developing nations can unlock the financial resources they need to build a brighter future.
How do global value chains and regional integration influence the economic growth strategies of developing nations in the near future?
Alright, let’s dive into how the global economic landscape is shifting, especially for our developing nations. It’s a story of interconnectedness, of opportunities, and yes, some tricky hurdles. We’ll explore how these countries can smartly navigate the waves of global value chains and regional integration to chart a course towards sustainable growth by 2025. It’s about being clever, being adaptable, and seizing the moment.
Opportunities and Challenges in Global Value Chains
The allure of global value chains (GVCs) is undeniable, offering developing nations a pathway to economic advancement. However, it’s not a simple walk in the park. Let’s look at both sides of the coin.
- Access to Markets: Participating in GVCs provides unprecedented access to global markets. This opens doors for developing nations to export goods and services, boosting their economies. For instance, consider Vietnam’s remarkable growth in the garment industry, fueled by its integration into GVCs. This has led to significant export revenues and job creation.
- Technological Upgrading: Exposure to GVCs can accelerate technological upgrading. Developing nations can learn from their partners, adopt new technologies, and improve their production processes. Think of the evolution of the electronics industry in countries like Malaysia, where participation in GVCs has driven significant technological advancements and skills development.
- Labor Standards: A significant challenge lies in ensuring fair labor standards. Developing nations often face pressure to compete on cost, potentially leading to exploitative labor practices. This requires careful monitoring, strong regulations, and international cooperation to ensure that workers are treated fairly and have decent working conditions.
Fostering Economic Integration Through Regional Trade Agreements, Economic growth strategies for developing countries trends 2025
Regional trade agreements are crucial for fostering economic integration and driving growth. They offer a stepping stone to global markets and create a more stable environment for trade and investment.
The future of AI, however, is a topic that requires careful consideration. While some see boundless possibilities, the potential for disruption is real. Exploring the ideas presented in The Future of AI Technology Is a Nightmare Trends 2025 A Looming Shadow. is essential to navigate the upcoming changes.
- African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA): The AfCFTA is a game-changer for Africa. By reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers, it aims to create a single market for goods and services, boosting intra-African trade. This initiative has the potential to unlock significant economic opportunities, fostering industrialization, and creating jobs across the continent. The success of AfCFTA hinges on effective implementation and addressing challenges like infrastructure deficits and trade facilitation.
- ASEAN Economic Community (AEC): The AEC is another powerful example of regional integration. By promoting free movement of goods, services, investment, and skilled labor, it has fostered economic growth and integration within Southeast Asia. This has created a more attractive environment for foreign investment and enhanced the region’s competitiveness in the global market.
Impact of Geopolitical Events and Trade Tensions
The global landscape is dynamic, and geopolitical events and trade tensions can significantly impact developing economies.The escalating trade tensions between major economies, the ongoing impact of global events, and shifting geopolitical alliances all influence the ability of developing nations to participate in GVCs. These events can disrupt supply chains, increase trade costs, and create uncertainty, making it harder for developing nations to attract investment and boost exports.
Navigating this complex environment requires flexibility, diversification, and strategic partnerships.
“The disruption of supply chains due to geopolitical tensions can lead to a decline in trade volumes and economic growth for developing countries.”
International Monetary Fund (IMF) analysis, 2023.
What are the crucial strategies for promoting inclusive growth and reducing poverty within the context of economic expansion in developing countries?

Source: turkiyetoday.com
It’s time to talk about something truly vital: ensuring that economic growth benefitseveryone*, not just a select few. We’re aiming for a future where prosperity lifts all boats, and that means tackling poverty head-on. This isn’t just a moral imperative; it’s smart economics. When more people have the resources to participate in the economy, the entire system thrives. Let’s dive into the practical steps needed to make this happen.
Social Safety Nets: Mitigating Poverty and Fostering Inclusive Growth
Social safety nets are the essential scaffolding that supports individuals and families when they face economic hardship. They are the lifeline that prevents people from falling into the abyss of poverty and gives them the chance to climb back up. These programs, when designed well, aren’t just about handouts; they’re investments in human capital and drivers of economic stability.
- Unemployment Benefits: Providing a financial cushion for those who lose their jobs is critical. It allows them to maintain basic needs while searching for new employment, preventing a downward spiral. Imagine a skilled worker in a manufacturing plant that shuts down. Unemployment benefits give them time to retrain, search for a new job, and avoid having to sell their assets or pull their children out of school.
This prevents a loss of human capital and supports the local economy.
- Food Assistance Programs: Hunger is a major barrier to economic participation. Food assistance programs ensure that families have access to nutritious food, allowing children to learn and adults to work. Think of a rural community where drought has devastated crops. Food assistance provides a critical buffer, allowing families to stay healthy and avoid selling off their livestock or land, preserving their future economic prospects.
- Conditional Cash Transfers (CCTs): These programs provide cash payments to families,
-but* with conditions attached, such as school attendance for children or regular health check-ups. CCTs are powerful tools for breaking the cycle of poverty by investing in human capital. For example, a CCT program might require parents to send their children to school and have them vaccinated to receive payments. This not only improves health and education outcomes but also encourages families to invest in their children’s future.
“Social safety nets are not a cost; they are an investment in a more stable, prosperous, and equitable society.”
Empowering Women and Girls: A Catalyst for Economic Expansion
Empowering women and girls is not just a matter of fairness; it is an economic necessity. When women have equal opportunities, economies grow faster and more sustainably. This requires a multi-pronged approach: education, access to healthcare, and economic opportunities.
- Education: Educating girls and women unlocks their potential and increases their economic participation. Educated women are more likely to be employed, earn higher incomes, and contribute to their communities. Think of a village where girls are traditionally kept home to help with chores. Investing in their education, through scholarships or by building schools, transforms the community. Educated women are more likely to start businesses, create jobs, and improve the overall standard of living.
- Access to Healthcare: Healthy women are more productive and can contribute more to the economy. This includes access to maternal healthcare, family planning, and other essential services. Imagine a country with high maternal mortality rates. Investing in healthcare, including prenatal care and skilled birth attendants, not only saves lives but also allows women to participate more fully in the workforce and contribute to economic growth.
- Economic Opportunities: Providing women with access to credit, land, and markets allows them to start businesses and earn a living. This includes addressing legal and cultural barriers that limit women’s economic participation. Consider a community where women are denied access to land ownership. Changing these laws, providing access to microloans, and supporting women entrepreneurs can dramatically increase their economic independence and contribute to overall economic prosperity.
Successful Case Studies: Poverty Reduction Programs in Action
Learning from success stories provides invaluable insights into what works and how. Let’s examine a few programs that have made a real difference in the lives of people in developing countries.
- The Bolsa Família Program (Brazil): This CCT program provides cash transfers to poor families,
-conditional* on children attending school and receiving regular health check-ups.Illustration: Imagine a vibrant photo depicting a Brazilian favela, with children in school uniforms walking to school, and mothers attending a health clinic. This image symbolizes the program’s success in promoting education and healthcare. Data shows a significant decrease in poverty rates and improved educational attainment among children.
Lessons Learned: Conditional cash transfers can be highly effective in reducing poverty and improving human capital, provided that they are well-targeted, efficiently administered, and supported by strong monitoring and evaluation systems.
- The Self-Employed Women’s Association (SEWA) (India): SEWA is a trade union of self-employed women workers, providing them with financial services, training, and advocacy.
Illustration: Picture a bustling marketplace in India, with women selling their products, participating in training workshops, and accessing microloans. This portrays the empowering effect of SEWA in providing women with financial independence. SEWA’s efforts have resulted in increased incomes, improved working conditions, and greater social recognition for women workers.
Lessons Learned: Supporting self-employment and empowering women entrepreneurs can significantly reduce poverty and create sustainable livelihoods. Providing access to finance, training, and market opportunities is key.
- The Grameen Bank (Bangladesh): This microfinance institution provides small loans to poor individuals, primarily women, without requiring collateral.
Illustration: Imagine a group of Bangladeshi women gathered around a table, receiving microloans from a Grameen Bank representative, and discussing their business plans. This image showcases the transformative power of microfinance. The Grameen Bank has helped millions of people escape poverty by enabling them to start their own businesses.
Lessons Learned: Microfinance can be a powerful tool for poverty reduction, particularly when targeted at women and combined with training and support services. Access to credit can enable people to start businesses, generate income, and improve their living standards.
Final Wrap-Up: Economic Growth Strategies For Developing Countries Trends 2025
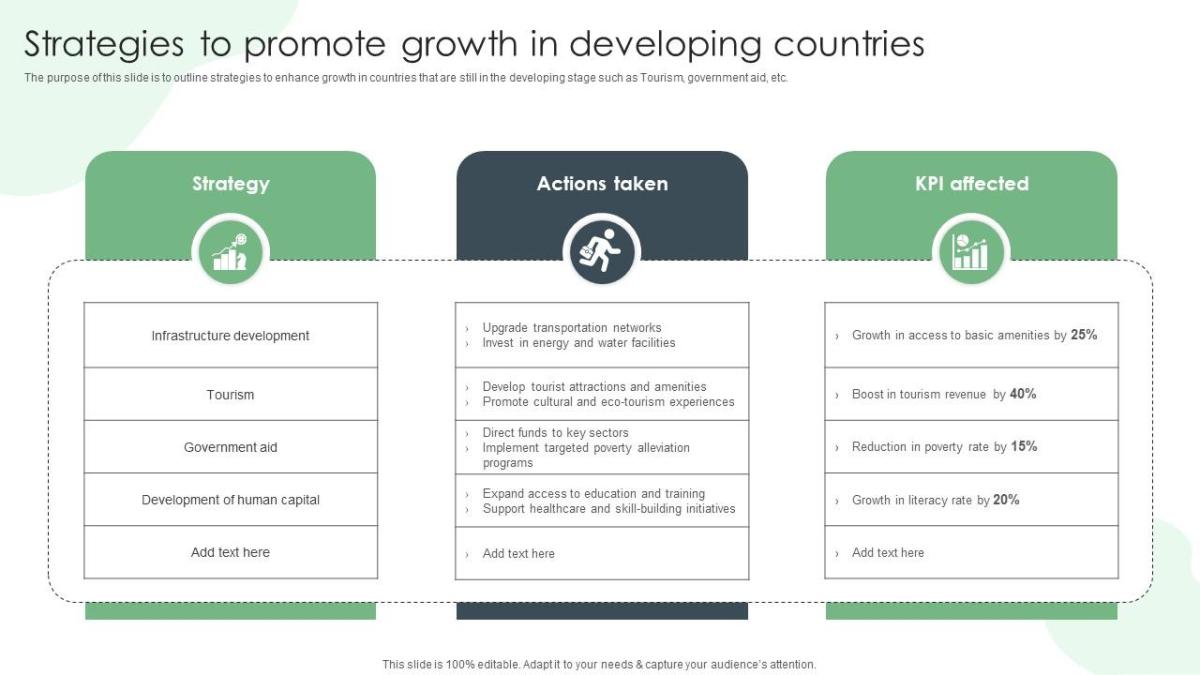
Source: slideteam.net
So, as we look towards 2025, the path is clear: a blend of bold policies, technological innovation, strategic financing, and a commitment to inclusive growth is not just desirable, it’s essential. The solutions are within our reach, and the potential for positive change is immense. Let’s embrace the challenge, learn from each other, and work together to build a future where economic prosperity and human flourishing go hand in hand.
The future is bright, and it’s waiting for us to create it. Let’s make it happen.